NMT是基因功能的活体检测技术,已被31位诺贝尔奖得主所在单位,及北大、清华、中科院使用。
NMT历史上的今天
2012年11月02日,河北师范大学崔素娟、王鹏利用NMT在Journal of Biological Chemistry 上发表了标题为A Na+ Ca2+ exchanger-like protein (AtNCL) involved in salt stress in Arabidopsis 的研究成果。
2016年11月02日,浙江大学李廷强、陶琦利用NMT在Journal of Experimental Botany 上发表了标题为The apoplasmic pathway via the root apex and lateral roots contributes to Cd hyperaccumulation in the hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii的研究成果。
期刊:Journal of Biological Chemistry
主题:Na+ Ca2+交换蛋白样蛋白(AtNCL)参与拟南芥的盐胁迫
标题:A Na+ Ca2+ exchanger-like protein (AtNCL) involved in salt stress in Arabidopsis
影响因子:4.773
检测指标:Ca2+流速
作者:河北师范大学崔素娟、王鹏
英文摘要
Calcium ions (Ca2+) play a crucial role in many key physiological processes; thus, the maintenance of Ca2+ homeostasis is of primary importance. Na+/Ca2+ exchangers (NCXs) play an important role in Ca2+ homeostasis in animal excitable cells.
Bioinformatic analysis of the Arabidopsis genome suggested the existence of a putative NCX gene, Arabidopsis NCX-like (AtNCL), encoding a protein with an NCX-like structure and different from Ca2+/H+ exchangers and Na+/H+ exchangers previously identified in plant. AtNCL was identified to localize in the Arabidopsis cell membrane fraction, have the ability of binding Ca2+, and possess NCX-like activity in a heterologous expression system of cultured mammalian CHO-K1 cells. AtNCL is broadly expressed in Arabidopsis, and abiotic stresses stimulated its transcript expression.
Loss-of-function atncl mutants were less sensitive to salt stress than wild-type or AtNCL transgenic overexpression lines. In addition, the total calcium content in whole atncl mutant seedlings was higher than that in wild type by atomic absorption spectroscopy. The level of free Ca2+ in the cytosol and Ca2+ flux at the root tips of atncl mutant plants, as detected using transgenic aequorin and a scanning ion-selective electrode, required a longer recovery time following NaCl stress compared with that in wild type.
All of these data suggest that AtNCL encodes a Na+/Ca2+ exchanger-like protein that participates in the maintenance of Ca2+ homeostasis in Arabidopsis. AtNCL may represent a new type of Ca2+ transporter in higher plants.
中文摘要(谷歌机翻)
钙离子(Ca2+)在许多关键的生理过程中起着至关重要的作用。因此,维持Ca2+稳态至关重要。 Na+ / Ca2+交换子(NCXs)在动物可兴奋细胞中的Ca2+稳态中起重要作用。
对拟南芥基因组的生物信息学分析表明,存在一个假定的NCX基因,拟南芥NCX样(AtNCL),编码一种具有NCX样结构的蛋白质,不同于先前在植物中鉴定的Ca2+/ H+交换子和Na+ /H+交换子。 AtNCL被确定位于拟南芥细胞膜部分中,具有结合Ca2+的能力,并在培养的哺乳动物CHO-K1细胞的异源表达系统中具有类似NCX的活性。 AtNCL在拟南芥中广泛表达,非生物胁迫刺激其转录本表达。
功能丧失的atncl突变体对盐胁迫的敏感性不如野生型或AtNCL转基因过表达株系。此外,通过原子吸收光谱法,整个atcl突变体幼苗中的总钙含量高于野生型。使用转基因水母发光蛋白和扫描离子选择电极检测到的atncl突变植物根尖细胞质中游离Ca2+和Ca2+通量的水平与野生型相比,在NaCl胁迫下需要更长的恢复时间。
所有这些数据表明,AtNCL编码一个Na+ / Ca2+交换子样蛋白,该蛋白参与拟南芥中Ca2+稳态的维持。 AtNCL可能代表高等植物中一种新型的Ca2+转运蛋白。
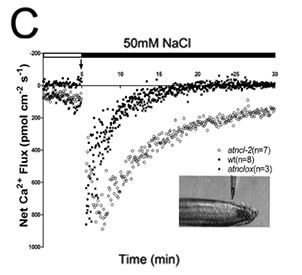
C)Ca2+ flux in the roots was measured by SIET. The bath [Ca2+] was 0.1 mM. After approximately 5 min at the resting level, 50 mM NaCl was added. The Ca2+ flux was then measured for about 30 min in the root tips (shown in the inset). The number of samples is shown in parentheses.
文章链接: http://www.jbc.org/content/287/53/44062.short
期刊:Journal of Experimental Botany
主题:根尖和侧根的无质子途径有助于镉在超级积叶景天中的过度积聚
标题:The apoplasmic pathway via the root apex and lateral roots contributes to Cd hyperaccumulation in the hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii
影响因子:5.354
检测指标:Cd2+流速
作者:浙江大学李廷强、陶琦
英文摘要
Although the significance of apoplasmic barriers in roots with regards to the uptake of toxic elements is generally known, the contribution of apoplasmic bypasses (ABs) to cadmium (Cd) hyperaccumulation is little understood.
Here, we employed a combination of stable isotopic tracer techniques, an ABs tracer, hydraulic measurements, suberin lamellae staining, metabolic inhibitors, and antitranspirants to investigate and quantify the impact of the ABs on translocation of Cd to the xylem in roots of a hyperaccumulating (H) ecotype and a non-hyperaccumulating (NH) ecotype of Sedum alfredii.
In the H ecotype, the Cd content in the xylem sap was proportional to hydrostatic pressure, which was attributed to pressure-driven flow via the ABs. The contribution of the ABs to Cd transportation to the xylem was dependent on the Cd concentration applied to the H ecotype (up to 37% at the highest concentration used). Cd-treated H ecotype roots showed significantly higher hydraulic conductance compared with the NH ecotype (76 vs 52 × 10–8 m s–1MPa–1), which is in accordance with less extensive suberization due to reduced expression of suberin-related genes.
The main entry sites of apoplasmically transported Cd were localized in the root apexes and lateral roots of the H ecotype, where suberin lamellae were not well developed. These findings highlight the significance of the apoplasmic bypass in Cd hyperaccumulation in hyperaccumulating ecotypes of S. alfredii.
中文摘要(谷歌机翻)
尽管人们普遍知道根部的质朴屏障对吸收有毒元素的重要性,但人们对质朴旁路(ABs)对镉(Cd)超富集的贡献却知之甚少。
在这里,我们采用了稳定的同位素示踪技术,ABs示踪剂,水力测量,粉刺蛋白片状染色,代谢抑制剂和止汗剂的组合,以研究和量化ABs对Cd向高积累根的木质素转运至木质部的影响。 H)景天草的生态型和非高积累(NH)生态型。
在H型生态系统中,木质部汁液中的Cd含量与静水压力成正比,这归因于通过AB的压力驱动流。 AB对Cd向木质部运输的贡献取决于应用于H生态型的Cd浓度(使用最高浓度时高达37%)。与NH生态型相比,Cd处理的H生态型根系显示出更高的水力传导性(76 vs 52×10–8 m s–1MPa-1),这与由于suberin相关基因表达减少而引起的泛化作用减弱有关。
非质态运输的镉的主要进入部位位于H型生态系统的根尖和侧根,那里的木栓质片状细胞发育不佳。这些发现突显了无性旁路在镉超积累中对苜蓿链球菌超积累生态型的重要性。
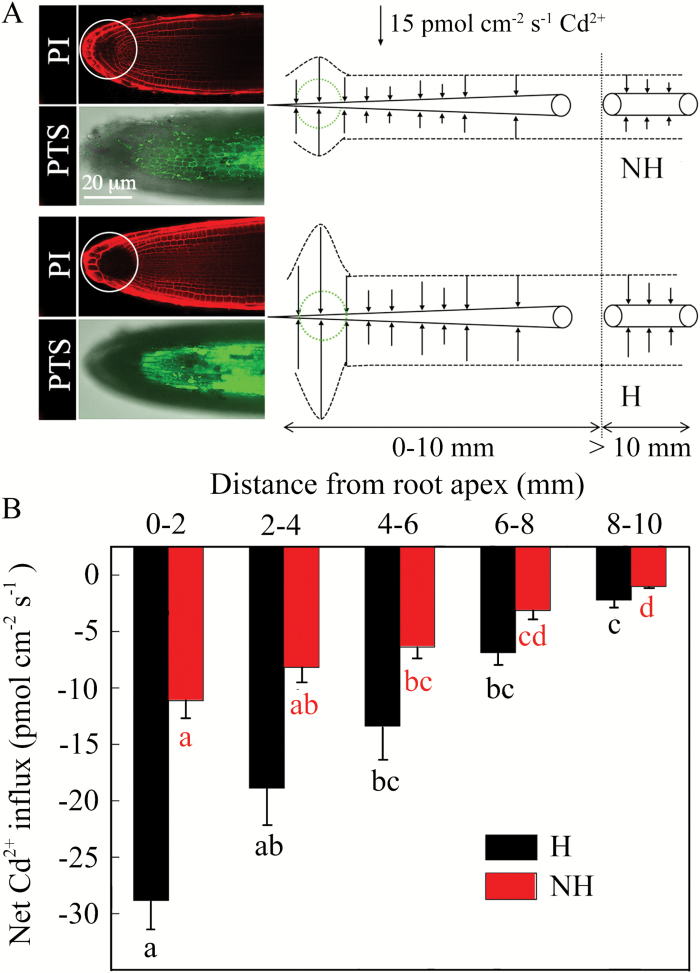
(B) The mean Cd fluxes in root cells of the H and NH ecotypes of S. alfredii at different distances from the root apex. The data are means ±SE (n=3). Different letters indicate significant differences within one ecotype
文章链接: https://academic.oup.com/jxb/article/68/3/739/2698905
