
期刊:Rice
主题:通气促进水稻根部Cd滞留
标题:Aeration Increases Cadmium (Cd) Retention by Enhancing Iron Plaque Formation and Regulating Pectin Synthesis in the Roots of Rice (Oryza sativa) Seedlings
影响因子:3.513
检测指标:O2、Cd2+流速
检测部位:距离根尖200微米、500微米,木质部
O2、Cd2+流实验处理方法:
3周龄水稻幼苗,50uM CdCl2及充空气(每小时30分钟)处理14天
O2、Cd2+流实验测试液成份:
0.01mM CdCl2,0.1mM KCl, 0.1mM CaCl2 and 0.3mM MES , pH 5.4
作者:浙江理工大学熊杰、李沪波
英文摘要
Aeration and water management increasingrhizosphere oxygen amount significantly promote rice (Oryza sativa) growth andyield, but the effect of root aeration on cadmium (Cd) toxicity andaccumulation in rice seedlings under hydroponic culture remains unclear.
Results showed that aeration promoted riceseedling growth and alleviated Cd toxicity. Transverse section discovered thatCd accelerated root mature and senescence while aeration delayed the mature andsenescence of roots. Non-invasive Micro-test Technology (NMT) showed thataeration increased net O2 and Cd2+ influxes on the surface of roots whiledecreased net Cd2+ influx in xylem. Perls blue staining showed that aerationand Cd treatments increased iron plaque formation on the surface of roots.Results of metal concentration analysis showed that besides increasing Cdretention in iron plaque, aeration also increasing Cd retention in the cellwall of rice roots. Cell wall component analysis showed that aeration not onlyincreased pectin content but also decreased pectin methylesterification degree(PMD) by increasing pectin methylesterase (PME) activity.
Conclusions
All of these results indicate that aerationnot only delays root mature and senescence but also increases Cd retention in rootsby enhancing iron plaque formation and regulating pectin synthesis in the rootsof rice seedlings.
中文摘要(谷歌机翻)
曝气和水分管理增加根际氧气量显着促进了水稻(Oryza sativa)的生长和产量,但根系曝气对水培过程中水稻幼苗镉(Cd)毒性和积累的影响仍不清楚。
结果表明,曝气促进了水稻幼苗生长,减轻了Cd的毒性。横切面发现Cd加速根成熟和衰老,而通气延迟了根的成熟和衰老。非损伤微测技术(NMT)显示,通气增加了根表面的净O2和Cd2+流入,同时降低了木质部中的净Cd2+流入。Perls蓝染色显示通气和Cd处理增加了根表面的铁斑块形成。金属浓度分析结果表明,除了增加铁斑块中Cd的保留外,还可以增加水稻根细胞壁中Cd的保留。细胞壁成分分析表明,通气不仅可以增加果胶含量,还可以通过增加果胶甲酯酶(PME)活性来降低果胶甲酯化程度(PMD)。
所有这些结果表明,通气不仅可以延缓根系成熟和衰老,还可以通过增强水稻幼苗根系中铁斑块形成和调节果胶合成来增加根中Cd的保留。
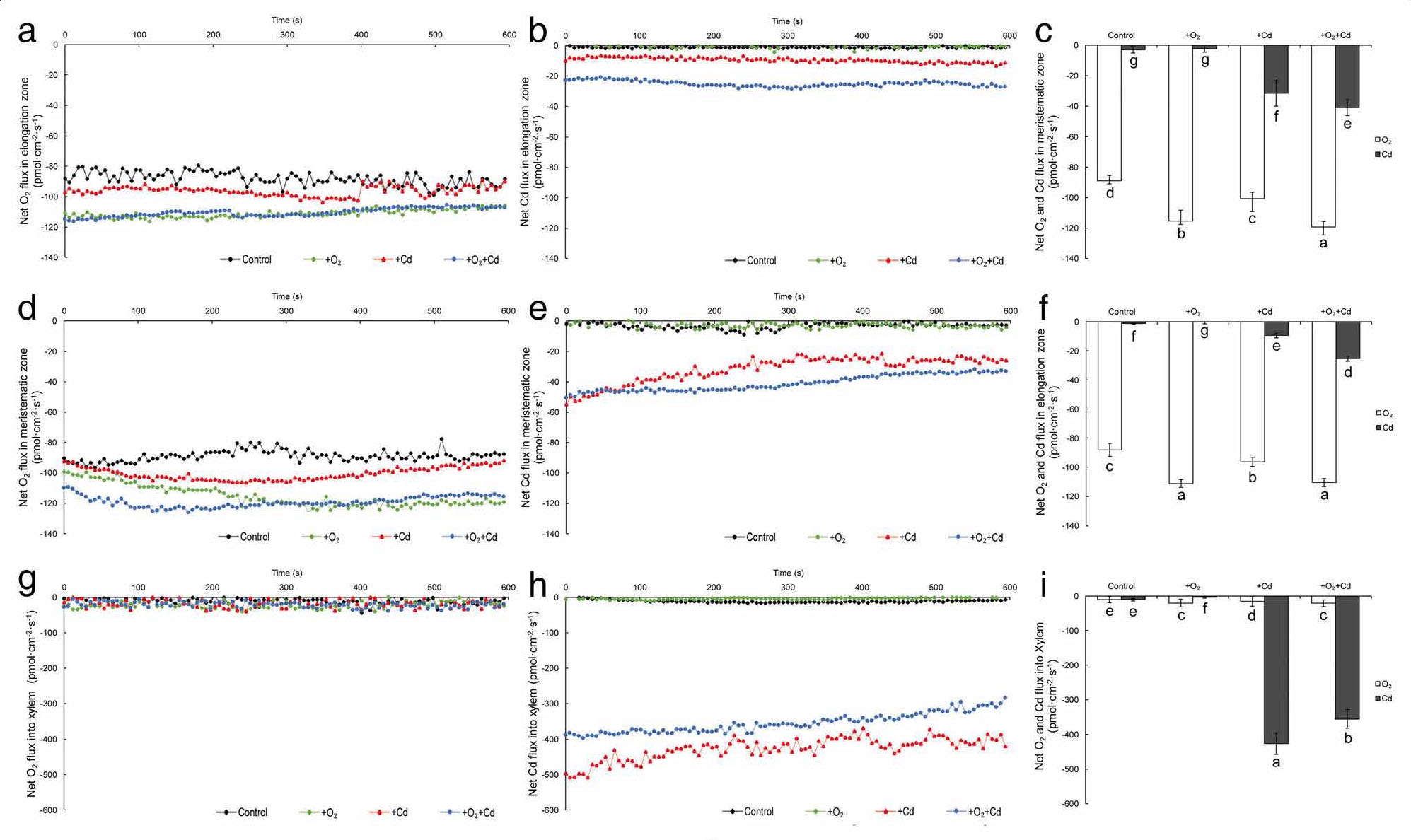
Fig. 3 Effects of aeration or/and 50 μM CdCl2 treatments on net O2 and Cd2+ fluxes in the roots of rice seedling. a Time-course of Net O2 flux on the surface of root at 500 μm from root apex (elongation zone); b Time-course of Net Cd2+ flux on the surface of root at 500 μm from apex (elongation zone); c Statistical results of steady-state net O2 and Cd2+ fluxes on the surface of root at 500 μm from apex (elongation zone); d Time-course of Net O2 flux on the surface of root at 200 μm from root apex (meristematic zone); e Time-course of Net Cd2+ flux on the surface of root at 200 μm from apex (meristematic zone); f Statistical results of steady-state net O2 and Cd2+ fluxes on the surface of root at 200 μm from apex (meristematic zone); g Time-course of Net O2 flux in the xylem of root at 500 μm from root apex (elongation zone); h Time-course of Net Cd2+ flux in the xylem of root at 500 μm from apex (elongation zone); i Statistical results of steady-state net O2 and Cd2+ fluxes in the xylem of root at 500 μm from apex (elongation zone). The 3-week-old rice seedlings under hydroponic culture were aerated with air pump (30 min per hour) in the absence or presence of 50 μM CdCl2 for 14 d. The values are means ± SE (n = 100). Different letters on bar indicate significant differences at P < 0.05
旭月版权所有,转载注明出处
