转自“中关村NMT联盟”
上周,中国农大郭岩课题组在Nature Communications在线发表题为Calcium-activated 14-3-3 proteins as a molecular switch in salt stress tolerance的研究成果。
Nature Commun. | 中国农大郭岩课题组揭示植物盐胁迫响应的调控新机制
研究揭示了14-3-3蛋白通过感受钙信号,选择性的结合和抑制SOS2和PKS5的激酶活性,并协同调控Na+/H+反向转运蛋白SOS1和质膜H+-ATPase活性,影响植物耐盐能力。
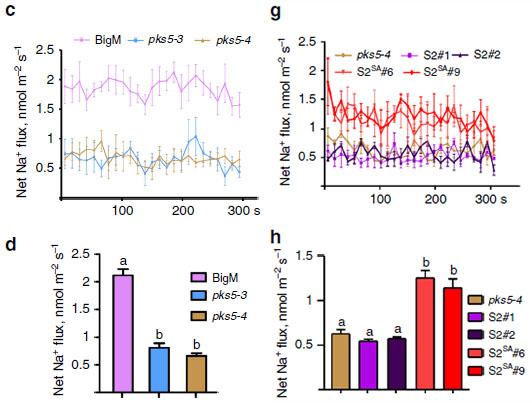
拟南芥根尖分生区Na+流结果
我们为您整理了利用非损伤微测技术(Non-invasive Micro-test Technology, NMT)研究SOS基因家族的盐胁迫文章。
-
Co-expression of SpSOS1 and SpAHA1 in transgenic Arabidopsis plants improves salinity tolerance. BMC Plant Biology, 2019, 19(1):74.
-
Overexpression of the PtSOS2 gene improves tolerance to salt stress in transgenic poplar plants. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2015, 13(7): 962-73.
-
Co-expression of the Arabidopsis SOS genes enhances salt tolerance in transgenic tall fescue (Festuca arundinacea Schreb.). Protoplasma, 2014, 251(1):219-31.
-
SOS1 gene overexpression increased salt tolerance in transgenic tobacco by maintaining a higher K+/Na+ ratio. Journal of plant physiology, 2012, 169(3): 255-261.
-
Nax loci affect SOS1-like Na+/H+ exchanger expression and activity in wheat. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2016, 67(3):835-44.
-
Haem oxygenase modifies salinity tolerance in Arabidopsis by controlling K+ retention via regulation of the plasma membrane H+-ATPase and by altering SOS1 transcript levels in roots. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2013, 64(2): 471-481.
-
Na+-H+ antiporter activity of the SOS1 gene, lifetime imaging analysis and electrophysiological studies on Arabidopsis seedlings. Physiologia Plantarum, 2009,137(2):155-65.
旭月版权所有,转载注明出处
